In the last post, we embarked on a journey through the realms of the circular economy, unravelling the possibilities of a sustainable future. Today, let us focus towards the broader global landscape, drawing insights from the recently explored circular solutions to confront the looming risks identified in the Global Risks Report 2024. As India seamlessly transitions from strategies fostering sustainability within local economies to navigating the intricate web of risks on a global scale, our quest for a resilient and transformative future gains momentum. Let us help bridge the gap between circular innovation and global risk mitigation, exploring how each facet contributes to shaping a world that is not only sustainable but also adept at navigating the challenges that lie ahead.
About- Global Risk Report 2024
In the intricate web of global challenges, The Global Risks Report stands as a compass, guiding leaders through the complexities of our interconnected world. Developed by the World Economic Forum in collaboration with Marsh McLennan, this comprehensive analysis is an essential read for business leaders, policymakers, academics, and those seeking to grasp the nuances of the global risk landscape.
Here is a summary of the key points from the document
- The document discusses the results of the World Economic Forum’s annual Global Risks Perception Survey which captures insights from nearly 1500 experts on major global risks.
- It finds that the majority of respondents have a predominantly negative outlook for the short-term future (next 2 years) and see the risks worsening over the long term (next 10 years).
- The top short-term risks are seen as misinformation/disinformation, extreme weather events, societal polarization, cyber insecurity, and interstate armed conflict.
- Economic risks like inflation and an economic downturn have risen in the short-term rankings.
- Over the long term, concerns grow about risks from climate change, new technologies like AI, and a fragmented geopolitical landscape hampering cooperation on global issues.
The report’s innovative temporal approach dissects global risks across three time frames, offering valuable insights for decision-makers in India. Chapter 1 scrutinizes the most severe risks over a concise two-year period, aiding leaders in addressing immediate crises. Simultaneously, Chapter 2 forecasts top risks emerging over the next decade, enabling strategic planning for long-term priorities. Chapter 3 discusses the suggested strategies towards mitigating the risks. The picture below depicts the global risk landscape and their interconnections.
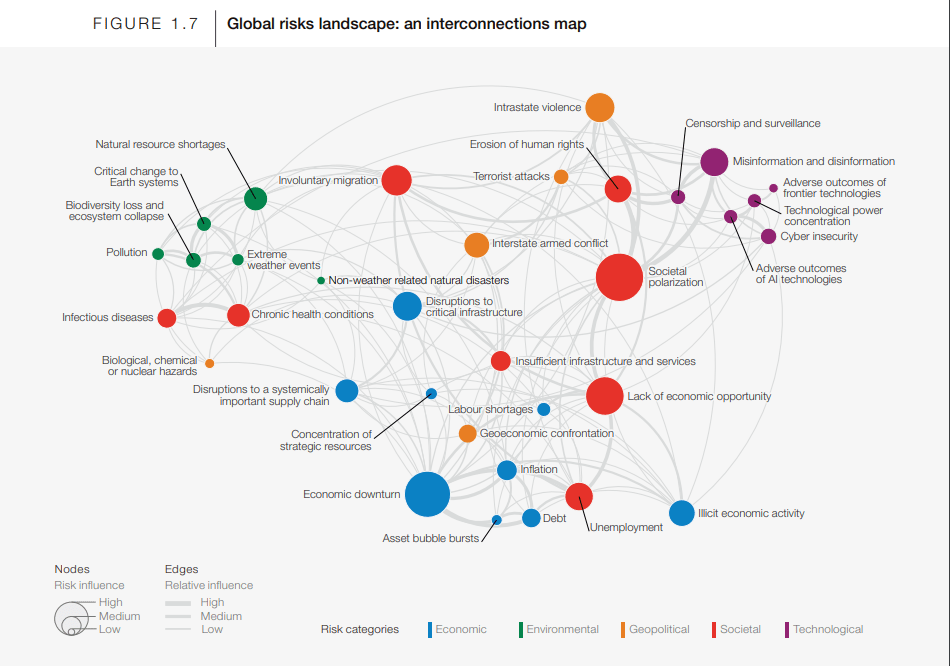
Here are the key points I gathered about medium- and long-term risks from the report:
- Over the 10-year time horizon, environmental and technological risks are expected to deteriorate the most in severity and dominate the risk landscape. Climate-related risks like extreme weather events, biodiversity loss, and critical changes to earth systems are among the top concerns.
- Adverse outcomes from artificial intelligence are anticipated to be one of the largest rises in severity, from #29 in the short term to #6 in 10 years, likely reflecting concerns about its systemic impacts.
- Misinformation/disinformation and cyber insecurity remain prominent technological risks, in the top 10 over the long term. Societal polarization is also a concern.
- Lack of economic opportunity rises in some stakeholder groups’ perceptions over the long run, suggesting it may be an underrated long-term risk.
- Younger respondents prioritize climate risks like biodiversity loss and earth system changes as more urgent over the short and long term, while the private sector sees most environmental risks materializing over a longer period. This mismatch in timing perceptions across groups could hamper coordination and risk mitigation efforts.
India Amidst a Deteriorating Global Outlook:
Recognizing these concerns, India is taking proactive steps, implementing strategic initiatives to fortify the nation against potential turbulence. The report identifies shifts in geostrategic dynamics, technological acceleration, material evolution, demographic bifurcation, and the emergence of new global conditions. India, aligning its policies with these shifts, stands resilient in the face of evolving global dynamics.
India’s Mitigation Strategies:
- Technological Resilience: India invests in technological innovation, enhancing its digital infrastructure to mitigate risks associated with rapid technological acceleration.
- Diplomatic Endeavors: Recognizing the impact of geopolitical shifts, India actively engages in diplomatic efforts, fostering international cooperation to navigate risks associated with global power dynamics.
- Sustainable Development Initiatives: Championing sustainability, India focuses on responsible resource use and environmental conservation, addressing challenges arising from material evolution.
- Demographic Planning: With a strategic lens on demographic challenges, India implements policies for skill development, education, and healthcare, harnessing the demographic dividend effectively.
India’s top 10 efforts for navigating some of the risks
- National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC): A comprehensive plan outlining India’s strategy for combating climate change, focusing on adaptation and mitigation measures.
- Swachh Bharat Abhiyan (Clean India Mission): A national cleanliness campaign aimed at achieving Open Defecation Free (ODF) in India and ensuring proper waste management.
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY): A financial inclusion program to ensure access to financial services, including banking and insurance, for all citizens.
- National Health Mission (NHM): A program to strengthen health systems in India, addressing issues related to maternal and child health, disease control, and healthcare infrastructure.
- Make in India: An initiative to promote manufacturing, innovation, and entrepreneurship in India, contributing to economic growth and job creation.
- Digital India: A campaign to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy by promoting digital literacy, technology adoption, and e-governance.
- Skill India: A program to empower the youth with skill development, aiming to enhance employability and bridge the gap between demand and supply of skilled workforce.
- Smart Cities Mission: Focused on urban development, this initiative aims to create sustainable and citizen-friendly cities equipped with modern amenities and infrastructure.
- Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY): A crop insurance scheme to provide financial support to farmers in the event of crop failure or damage due to natural calamities.
- UDAN (Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik): A regional airport development and “make flying affordable” scheme to enhance air connectivity to underserved and unserved airports.
Critical challenges for India
It’s important to note that opinions and perspectives on this matter can be diverse, and the information provided here may not capture the full spectrum of views. Here are some potential criticisms that India, like any other nation, could face:
- Climate Change Action Challenge: Navigating the complex landscape of climate change mitigation remains a challenge, demanding a careful balance between economic development and sustainable practices.
- Air Quality and Pollution Challenge: The challenge lies in effectively tackling air pollution, particularly in urban areas, necessitating robust strategies to improve air quality and protect public health.
- Natural Resource Management Challenge: Sustainably managing India’s rich natural resources poses a challenge, requiring careful planning to ensure responsible exploitation and preservation for future generations.
- Urbanization Management Challenge: Effectively managing the rapid pace of urbanization is a challenge, demanding comprehensive planning and execution to balance infrastructure needs with environmental sustainability.
- Waste Management Challenge: Addressing the challenge of waste management and pollution requires more effective waste disposal systems and a commitment to implementing robust recycling and waste reduction strategies.
- Public Health Preparedness Challenge: Enhancing public health infrastructure and preparedness is a pressing challenge, particularly in the face of global health risks, necessitating comprehensive and adaptive strategies.
- Inequality and Vulnerability Challenge: The challenge lies in addressing social inequalities comprehensively, ensuring that efforts to mitigate global risks consider and uplift vulnerable populations that may bear a disproportionate burden.
- International Cooperation Challenge: Balancing national interests with active engagement in international cooperation efforts presents a challenge, emphasizing the need for collaboration to address shared global challenges effectively.
- Technological Adaptation Challenge: Rapidly adapting and integrating emerging technologies, especially in areas like cybersecurity and artificial intelligence, is a challenge that demands continuous innovation and technological advancement.
Recognizing these challenges provides an opportunity for constructive dialogue and concerted efforts to find sustainable solutions and drive positive change.
Shaping India’s Future:
Looking ahead, India is poised to lead in several transformative trends on the global stage:
- Technology Hub: India emerges as a global technology hub, leading advancements in artificial intelligence, data analytics, and cybersecurity.
- Renewable Energy Revolution: With ambitious renewable energy targets, India is set to lead the world in sustainable energy solutions, contributing significantly to the global fight against climate change.
- Innovation in Healthcare: As a pioneer in affordable healthcare solutions, India is expected to lead innovations in telemedicine, biotechnology, and pharmaceuticals.
- Smart Cities and Urban Transformation: India’s focus on smart city initiatives will drive urban transformation, integrating technology for efficient resource use, transportation, and infrastructure.
- Agricultural Innovation: Leveraging technology and sustainable practices, India is set to lead in agricultural innovation, ensuring food security and resilience in the face of global challenges.
As the world grapples with uncertainties, India’s proactive stance, as mirrored in The Global Risks Report 2024, not only positions the nation as a respondent but as a trailblazer. In navigating risks and embracing opportunities, India emerges as a beacon, shaping a resilient and transformative future.
In wrapping up our exploration of circular economies and global risks, India isn’t just keeping up—it’s leading the charge towards a stronger and better future. From taking on sustainability challenges to getting ready for potential global issues, India is set on making a positive change. With smart solutions and thoughtful policies, India is on track to lead in technology, sustainable development, and innovation. In a world full of challenges and opportunities, India’s journey is like a shining example of resilience and progress. As we embrace circular ways of doing things and prepare for global changes, let’s take a cue from India’s approach—a future where innovation and sustainability go hand in hand.


Leave a comment